The healthcare industry has come a long way, from in-person consultation and paper-based records to AI-driven diagnostics. However, the industry still grapples with fragmented systems, rising healthcare costs, and sub-par treatments. Reports indicate that 80% of healthcare data remains unstructured and underutilized, while 20% of misdiagnoses stem from delayed or inaccurate information. That is where IoT in healthcare steps in, turning the tide by offering remote monitoring, predictive analytics, and precision-driven care.
The Internet of Things in healthcare is proving to be a game-changer that offers real-time patient monitoring, manages hospital workflows efficiently, and enhances medical decision-making. The worldwide IoT in Healthcare market size is expected to grow from $127.7 billion in 2023 to $289.2 billion by 2028.
From wearable devices that track vital signs to smart hospital management systems, IoT is driving digital transformation in healthcare like never before. In this blog, we will explore how the amalgamation of healthcare and IoT is redefining patient care through state-of-the-art technologies and connected healthcare solutions.
What is IoT in Healthcare?
IoT technology in healthcare connects medical devices such as insulin pumps, wearables, and sensors to the internet for hassle-free data sharing. These devices gather a patient’s real-time health metrics and transfer them to healthcare providers to automate care. But what’s the importance of IoT in healthcare? What purpose does it solve?
Well, to answer the above question, we will take an example.
Suppose an elderly patient with chronic heart disease wears a smart patch that regularly monitors heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This data is then automatically sent to their doctor’s system. If the patch detects a sudden drop in oxygen or a heart rate spike, the system instantly alerts the doctor. The doctor can then remotely assess the patient and intervene before a severe crisis occurs.
This presents the significant impact of IoT in healthcare with proactive and real-time monitoring. Additionally, it reduces hospital readmissions and allows for personalized, timely interventions. Ultimately, IoT for healthcare improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
How Does Internet of Things in Healthcare Work?
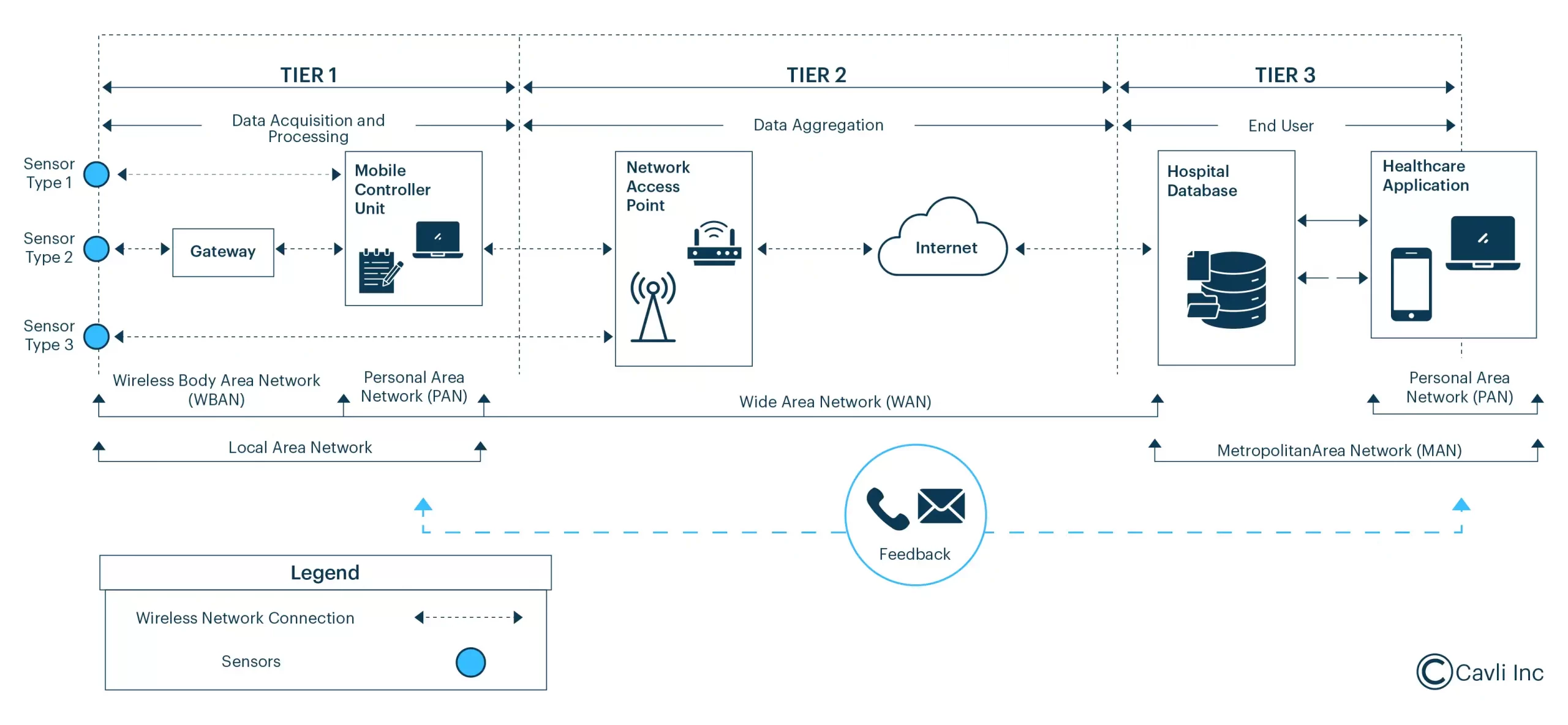
As we have discussed the role of IoT in healthcare, it’s also necessary to know how it functions. Understanding the functionality will give you a clear picture of how IoT connects medical devices and provides seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers.
There are various IoT devices used in healthcare (like glucose monitors or pulse oximeters) to gather patient data. This data then travels through Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or 5G to cloud platforms. AI algorithms analyze trends, flag risks, and alert doctors. For example, a smart inhaler tracks asthma triggers and sends alerts to an IoT-powered healthcare mobile app that prompts patients to take necessary precautions.
IoT implementation in healthcare processes includes many key steps. The essential steps are discussed below:
1. Data Gathering
IoT medical devices gather complete healthcare data from patients by continuously monitoring them 24/7.
2. Data Transmission
The collected data is then securely sent to healthcare systems through encrypted channels for analysis.
3. Data Analysis
Healthcare professionals study the processed data to comprehend patient health and improve treatment effectiveness.
4. Data-Driven Insights
Providers utilize real-time data to make informed decisions and adjust treatments accordingly.
IoT Health Monitoring: Data Flow Structure
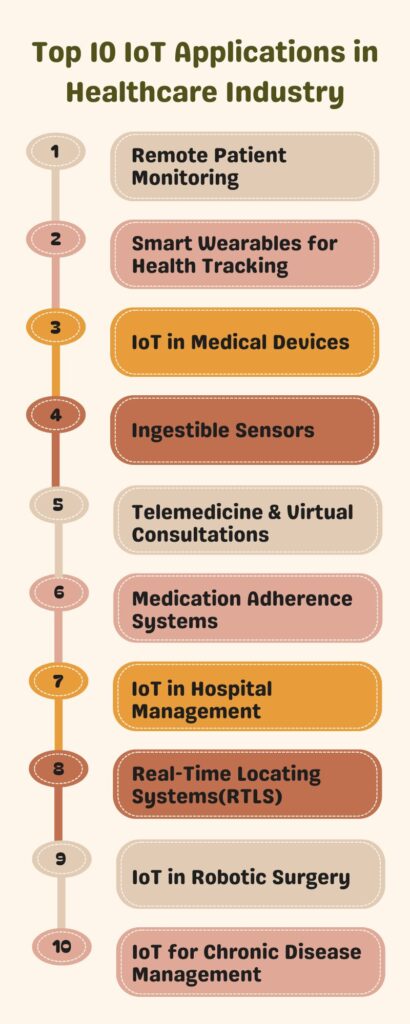
Top 10 IoT Applications in Healthcare Industry
You must have comprehended how IoT in the healthcare industry works by now. Now, let’s explore IoT use cases in healthcare that are transforming the sector with innovative smart healthcare solutions. From remote monitoring to robotic surgery, these applications of IoT in healthcare are taking patient care to a new level.
1. IoT for Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Doctors can track a patient’s vital signs with IoT devices for remote patient monitoring. Moreover, healthcare professionals can use data from wearable sensors and connected devices to monitor heart rate, oxygen levels, and other metrics. This helps in timely interventions, reduces hospital visits, and improves patient care.
For Example: An implanted cardiac monitor sending arrhythmia alerts to clinics in real-time.
2. Smart Wearables for Health Tracking
There are IoT-enabled wearables that help users to track their fitness goals and manage chronic conditions. According to a study, 92% of smartwatch wearers use wearable devices for health or fitness monitoring. These IoT wearable devices connect with healthcare systems for early detection and preventive care. Let’s look at some smart wearables in healthcare below–
-
Fitness Bands
Fitness bands track steps, calories, sleep patterns, and activity levels. They help users stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
For Example: Fitbit guides users to personalized fitness goals.
-
Heart Rate Monitors
Heart rate monitors detect irregularities and provide early warnings of potential heart issues. Athletes and heart patients use these devices to keep their cardiovascular health in check.
For Example: Apple Watch detecting atrial fibrillation.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
30+ million Americans are facing issues related to diabetes. Using CGM, diabetic patients can track blood sugar levels, which helps them to manage their glucose levels. CGM devices reduce the need for frequent finger pricks.
For Example: Dexcom alerting diabetics to glucose spikes.
-
Hearables
Smart hearing aids and earbuds with IoT capabilities improve auditory experiences. They filter background noise, provide real-time translation, and even track biometric data.
For Example: Bose SoundControl adjusts to environments.
-
Moodables
Mood-aware IoT devices track emotional states using brainwave sensors. These IoT-connected devices help manage stress, anxiety, and depression by providing personalized mental health insights.
For Example: Muse headbands use EEG (electroencephalogram) to track relaxation.
3. IoT in Medical Devices
IoT in medical sector transforms traditional practices into smart, connected tools that enhance patient care and operational agility.
-
IoT-enabled Ventilators
These ventilators adjust airflow based on patient data to ensure optimal respiratory support. They help manage critical care more effectively.
For Example: Medtronic ventilators reduce lung injury risks.
-
Infusion Pumps
IoT-connected infusion pumps deliver medication at precise doses. They reduce errors and ensure safe drug administration in hospitals and home care settings.
For Example: BD Alaris prevents overdose errors.
-
Connected Inhalers
One of the examples of IoT in healthcare is smart inhalers. It tracks medication use and sends reminders to patients. They help manage respiratory conditions like asthma.
For Example: Propeller Health maps asthma flare-ups.
-
Connected Contact Lenses
IoT-powered contact lenses monitor eye health and adjust vision automatically. It is one of the significant IoT healthcare use cases that offer a futuristic approach to eye care.
For Example: Google’s prototype lens for diabetics.
4. Ingestible Sensors
Sounds confusing? Well, these are tiny sensors that are swallowed like pills to monitor health issues from inside the body. Ingestible sensors track medication absorption, detect diseases, and send instant updates to doctors.
For Example: Proteus Digital Health tracks medication in schizophrenia patients.
5. Telemedicine & Virtual Consultations
IoT in telemedicine app development provides remote doctor consultations via video calls. Connected medical devices allow physicians to monitor patient health, diagnose, and prescribe treatments without in-person visits.
For Example: Teladoc integrates blood pressure cuffs into video calls.
6. Medication Adherence Systems
Mobile healthcare apps benefit healthcare industry in many ways. Businesses can integrate IoT in medical apps to remind patients to take medication on time and correctly.
-
Smart Pill Dispenser
One of the popular IoT examples in healthcare is the usage of Smart pill dispensers. These dispensers remind patients to take their pills on time and alert caregivers if doses are missed.
For Example: Hero sends reminders via app.
-
Intelligent Insulin Pens
These pens track insulin doses, record injection times, and sync with mobile apps for better diabetes management.
For Example: NovoPen tracking diabetic regimens.
-
Smart Thermometers
IoT thermometers provide instant readings, detect fever trends, and send alerts to doctors. They help monitor infections and other illnesses.
For Example: Kinsa mapping illness outbreaks.
-
Healthcare Charting
IoT in healthcare automates medical record updates that reduce paperwork and ensure accurate patient history tracking for better care.
For Example: Suki AI reduces administrative burnout.
7. IoT in Hospital Management System (HMS)
The Internet of Things can be helpful in many healthcare operations. It can automate patient tracking, manage assets, and perform predictive medical equipment maintenance to reduce inefficiencies and improve care delivery.
8. Real-Time Locating Systems(RTLS)
With the assistance of RTLS, caregivers can immediately locate the position of patients, especially during emergency and critical circumstances. Integrating RTLS allows healthcare organizations to seamlessly manage and track essential medical resources like equipment, medications, and supplies.
For Example: GE Healthcare’s tags cut ventilator search time by 50%.
9. IoT in Robotic Surgery
IoT for robotic surgery enhances precision and minimizes risks. Surgeons control robotic arms remotely to ensure accuracy in delicate procedures while reducing recovery time.
For Example: Da Vinci Surgical System, which performs complex procedures with greater precision and less invasiveness.
10. IoT for Chronic Disease Management
IoT in medical diagnostics helps manage long-term conditions by continuously monitoring symptoms and providing real-time alerts.
For Example: Cohero Health alerting asthma patients to pollen zones.
Key Benefits of IoT in Healthcare
As a business leader, knowing the crucial benefits of IoT for patient care is essential. This will help you build an IoT-connected healthcare app that provides real-time patient monitoring, accurate data analysis, and quick emergency response. So, let’s move ahead and see the imperative advantages of IoT in healthcare.
-
Monitor Patients in Real-Time
IoT devices track vital signs, detect abnormalities, and send instant alerts to healthcare providers. This enables proactive care, reduces hospital readmissions, and helps manage chronic conditions more effectively.
1. Data Assortment and Analysis
One of the striking benefits of the Internet of Things is that it collects and analyzes vast amounts of health data. Apart from that, AI agents in healthcare help doctors predict diseases, personalize treatments, and enhance patient outcomes with precision.
2. Manage Drugs and Equipment
IoT in Smart inventory systems tracks drug usage and medical equipment availability. This prevents shortages, reduces wastage, and ensures timely replenishment of essential supplies.
3. Quick Health Checks Anywhere
Wearable IoT devices and remote monitoring allow patients to check their health status from anywhere. This reduces the need for frequent hospital visits and promotes preventive care.
4. IoT Connectivity in Healthcare
Using the Internet of Things in hospitals facilitates seamless connectivity between devices, which ensures smooth data exchange across hospitals, clinics, and caregivers. This improves coordination, minimizes errors, and enhances overall healthcare efficiency.
5. Data-Driven Decision-Making
IoT enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions based on real-time insights. Predictive analytics help optimize treatments and reduce unnecessary procedures.
6. Faster Emergency Response
IoT-connected ambulances and emergency rooms provide patient data before arrival. This helps doctors prepare in advance and speed up life-saving interventions.
7. Simplify Care for the Elderly
Smart sensors and wearable devices help seniors stay independent while ensuring their safety. Caregivers receive instant alerts for falls, irregular heart rates, or missed medications.
Essential Features of Healthcare IoT Applications
Healthcare IoT applications rely on critical features like real-time data collection, AI-driven insights, and strong security measures. These ensure seamless patient monitoring, interoperability with existing systems, and scalable solutions for better healthcare outcomes.
Real-Time Data Collection
IoT devices continuously track vital signs, medication adherence, and patient activity. This real-time monitoring enables early detection of health issues, reduces emergency visits, and improves patient care through timely medical interventions.
Interoperability with EHR Systems
Seamless integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) ensures patient data is easily accessible across healthcare providers. This eliminates data silos, enhances collaboration, and allows for a more holistic approach to patient treatment.
AI and IoT in Healthcare Apps
AI and IoT in healthcare analyze vast amounts of patient data to detect patterns, predict diseases, and recommend treatments. AI in healthcare enhances diagnostics, automates workflows, and helps doctors make data-driven decisions for personalized care.
Scalability using Cloud Computing
Cloud-based IoT solutions provide unlimited scalability, allowing hospitals to expand their digital capabilities without infrastructure limitations. Cloud storage ensures secure, remote access to patient data, making healthcare services more efficient and flexible.
Security and Compliance
IoT apps for healthcare must comply with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to protect patient data. End-to-end encryption, secure data transmission, and multi-factor authentication help prevent breaches and ensure patient privacy.
How to Deploy Internet of Things in Healthcare?
Implementing IoT in healthcare requires careful planning, secure infrastructure, and continuous monitoring. It’s a complex process; therefore, as a healthcare entity, you should take the assistance of an experienced IoT app development company to carry out the implementation process.
A structured approach ensures seamless integration, optimized performance, and compliance with industry regulations, leading to better healthcare outcomes.
1. Evaluate the Existing System (1-3 Months)
Assess your current healthcare processes, IT infrastructure, and data management systems. It will help you to identify gaps and determine the right IoT solutions for healthcare that align with medical workflows to enhance agility.
2. Plan Strategy and Set Goals (1-2 Months)
After that, clearly define objectives. What do you want from IoT-based solutions such as remote patient monitoring, VR in healthcare, or hospital automation? Setting measurable goals ensures IoT adoption aligns with healthcare needs, enhances patient care, and delivers cost-effective results.
3. Build a Strong Network Infrastructure (3-6 Months)
A reliable IoT infrastructure requires secure, high-speed connectivity. Hospitals must invest in robust Wi-Fi, 5G, and edge computing to support real-time data exchange and device interoperability.
4. Ensure Security and Compliance (2-4 Months)
Implement encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular audits to protect patient data. Adhering to regulatory standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA guidelines ensures data integrity and legal compliance.
5. Build and Test IoT Solutions (6-12 Months)
Before full deployment, IoT solutions must be tested for reliability and performance. Simulating real-world scenarios helps fine-tune device functionality and ensures seamless integration with existing healthcare systems.
6. End-to-End Development (3-6 Months)
Develop IoT applications with user-friendly dashboards, AI-driven analytics, and cloud compatibility. A well-structured development phase ensures long-term sustainability and efficiency in healthcare operations.
7. Monitoring and Improvement (Ongoing)
IoT in healthcare requires continuous monitoring to detect faults, optimize performance, and prevent cyber threats. Regular updates and AI-driven predictive maintenance enhance system efficiency and data accuracy.
Evaluating the Cost of Implementing IoT in Healthcare
The cost of IoT in healthcare fluctuates. It depends on the hardware used, software type, cloud infrastructure, compliance, and integration complexity. However, the estimated cost of IoT implementation in healthcare typically ranges between $30,000 to $300,000+.
Several factors, such as device type, data storage needs, and AI capabilities, influence the total cost to develop a healthcare app. A well-planned strategy ensures cost efficiency and maximum ROI.
Initial setup can be pricey, but long-term savings from better patient management are substantial. It’s an investment that can benefit hospital owners, professionals, and investors in the long run.
IoT Healthcare Cost Breakdown
| Implementation Level | Estimated Cost Range | Inclusions |
| Basic IoT Setup | $30,000 – $70,000 | Wearables, remote patient monitoring, basic data collection, and cloud storage |
| Mid-Level Integration | $70,000 – $140,000 | EHR integration, AI-driven analytics, advanced data processing, and security measures |
| Enterprise-Grade IoT Solutions | $140,000 – $300,000+ | Full-system IoT integration, AI automation, blockchain security, real-time analytics, and large-scale cloud infrastructure |
Common IoT Healthcare Implementation Challenges
While IoT in healthcare offers several benefits and features, it also comes with mounting challenges like security risks, integration issues, and compliance hurdles. In this section, we will discuss IoT healthcare implementation challenges that can deter seamless adoption.
Data Security & Privacy
IoT devices generate vast amounts of sensitive patient data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
Integration with Multiple Devices & Protocols
Different IoT devices use various communication protocols, making seamless integration challenging.
Data Overload & Accuracy
Massive volumes of patient data can overwhelm healthcare providers, leading to misinterpretation or delays in decision-making.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare IoT solutions must adhere to strict regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA guidelines.
Costs Involved
Implementing IoT in healthcare involves significant investment in hardware, software, security measures, and infrastructure upgrades.
How to Tackle IoT Challenges in Healthcare Effectively
IoT in healthcare faces challenges like security risks, data overload, and integration issues. Overcoming these challenges requires 5G connectivity, edge computing, AI-driven diagnostics, blockchain security, and personalized medicine for seamless operations and better patient outcomes.
1. Encrypted Data Security
Implement end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and blockchain technology to safeguard patient data. Regular security audits and real-time threat detection help prevent cyberattacks and ensure data privacy.
2. Seamless Protocol Integration
Adopting FHIR, HL7, and MQTT protocols ensures interoperability between IoT devices and healthcare systems. Hire IoT developers that will use cloud-based APIs to further simplify data exchange and enhance system compatibility.
3. AI-Powered Data Management
AI-powered analytics filter and prioritize relevant patient data, reducing unnecessary alerts. Edge computing processes data locally, ensuring only essential information is sent to healthcare providers, improving accuracy and efficiency.
4. Automated Regulatory Compliance
Implement HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA-compliant security frameworks. Automating compliance tracking, maintaining audit logs, and conducting regular assessments to ensure adherence to healthcare regulations and avoid legal risks.
5. Cost-effective IoT Solutions
Using cloud computing, open-source platforms, and modular IoT architectures helps reduce upfront costs. Investing in predictive maintenance and as-a-service models minimizes operational expenses, making IoT adoption more cost-effective.
Key IoT in Healthcare Future Trends to Watch
The future of IoT in healthcare is evolving with advancements like 5G, AI-driven diagnostics, edge computing, and blockchain security. These innovations are set to enhance patient care, optimize hospital operations, and create a more connected healthcare ecosystem.
5G Impact on Healthcare IoT
5G enables ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity that improves real-time remote monitoring, robotic surgeries, and telemedicine services. With better network reliability, healthcare providers can access patient data instantly.
Edge Computing for Reduced Latency
Edge computing processes data closer to the source, which reduces delays and bandwidth dependency. This ensures real-time decision-making in critical applications like ICU monitoring and wearable health devices.
AI-Driven Predictive Diagnostics
One of the key IoT healthcare trends is predictive diagnostics. AI-powered IoT devices analyze patient data to detect early signs of diseases. By identifying potential health risks before symptoms appear, AI enhances preventive care and reduces hospitalization rates.
Blockchain for Secure Health Data Exchange
Blockchain enhances security by creating tamper-proof, decentralized health records. It ensures safe data sharing between providers while maintaining patient privacy, reducing fraud, and improving compliance with healthcare regulations.
Personalized Medicine
IoT and AI provide customized treatment plans based on individual patient data, genetic factors, and real-time health tracking. This approach enhances medication effectiveness, reduces side effects, and improves long-term health outcomes.
How Can SparxIT Help You Integrate IoT Technology in Healthcare?
SparxIT has expertise in seamless IoT integration for healthcare. As a leading healthcare app development company, we offer custom solutions that can be easily integrated into your apps smart wearables, and other connected IoT devices. Apart from that, we believe in secure and transparent data management. Our expertise in AI, cloud computing, and blockchain ensures a future-ready healthcare system.
We focus on HIPAA-compliant app development, interoperability, and real-time analytics to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. We deliver scalable, cost-effective IoT solutions tailored to your healthcare needs from strategy to deployment.

Partner with Experts
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Role of IoT in Healthcare?







IoT in healthcare improves patient monitoring, hospital efficiency, and data-driven decision-making through remote consultations and automated workflows. Additionally, it ensures faster diagnoses, better treatments, and reduced operational costs for patients.
What is the benefit of an IoT-enabled medical device?












IoT-enabled devices continuously monitor health data, providing real-time alerts for critical conditions. They improve patient care, reduce hospital visits, and enhance treatment precision that ensures better management of chronic diseases.
What is the future scope of IoT in medical industry?












IoT will drive AI-powered diagnostics, 5G-enabled remote care, blockchain-secured health records, and personalized treatments. As healthcare becomes more connected and data-driven, IoT will continue transforming patient care, hospital management, and medical research.
What are the challenges of IoT in healthcare?












Key challenges include data security risks, device interoperability issues, high implementation costs, and regulatory compliance. Ensuring HIPAA/GDPR compliance, robust cybersecurity, and seamless integration is crucial for successful IoT adoption in healthcare.
How much does it cost to integrate IoT into healthcare systems?












IoT integration costs vary based on device complexity, software development, security measures, and cloud infrastructure. A basic system may start at $30,000, while advanced, AI-powered solutions can cost $300,000, depending on scalability.