The healthcare sector is undergoing a major digital transformation driven by cloud AI, telemedicine, IoT devices, and electronic health records (EHRs). But this digitization has also increased the industry’s susceptibility to data breaches and cyberattacks. According to reports, in 2024, the protected health information of 276,775,457 people was leaked or stolen. That is about 758,288 records every single day!
Cybercriminals have hacked interconnected devices from infusion pumps and MRIs to video cameras and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. These devices include protected healthcare information (PHI) that needs to be secured.
Hospitals, clinics, administration, and even patients require robust cybersecurity in healthcare to ensure data safety and shield all of their equipment from misuse. The good news is that you can hire a cybersecurity services provider to protect medical equipment that meets the criteria for PHI, or personally identifiable information (PII), from cyber threats.
This blog discusses the need for cybersecurity in the healthcare industry, challenges in protecting patient data, and offers solutions to create a robust defense system for hospitals and clinics.
What is Cybersecurity in Healthcare?
Cybersecurity in healthcare is all about protecting patients’ personal and medical information from getting into the wrong hands. Healthcare providers manage highly sensitive data like patient histories, prescriptions, and billing information, which are prime targets for cybercriminals. These data are crucial for hackers who want to steal, leak, or tamper with them.
With cybersecurity for healthcare, organizations may use tools like Wireshark, OpenVAS, Okta, VeraCrypt, etc., to keep that data private and secure. It’s not just about implementing the technology; it’s also about keeping everything running smoothly, identifying threats early, and being ready if something goes wrong.
Why are Cyber Attacks in Healthcare Rapidly Increasing?
Historically, cyberattackers have primarily targeted the healthcare sector. But why? There have to be some strong reasons, right? Indeed. The healthcare industry holds highly sensitive patient data such as names, addresses, medical records, etc. Threat actors can utilize this data for identity theft, fraud, or blackmail. Let’s look at some reasons below.
1. Unsecured Attack Surface
Many third parties have access to sensitive patient data in hospital settings. Healthcare organizations also deal with various connected medical devices (Internet of Medical Things, or IoMT) that may not have sufficient endpoint security. Additionally, an increase in virtual doctor’s visits (telehealth) has generated an even bigger attack surface for attackers.
2. High Demand for PHI Data
Threat actors value PHI data highly as it contains a wealth of personal information that can be utilized for identity theft, healthcare insurance fraud, and other malicious actions. Because of this, each medical record sells for hundreds of dollars on the dark web, which is far more than, say, a stolen credit card.
3. Breaches Disrupt Operations
Patient data that may be needed to carry out vital procedures is inaccessible. Furthermore, PHI disclosure is punishable by steep fines under privacy laws like HIPAA. Penalties for HIPAA violations can reach up to $1.81 million annually.
4. Aging Legacy Systems
Many healthcare entities continue to use outdated legacy systems that were not designed to withstand today’s cyber threats. These systems don’t receive regular updates and lack modern security features, making them easy targets in a digital world.
5. People-Centric Vulnerabilities
Human mistakes, from overworked employees clicking on phishing emails to using weak passwords, are a hacker’s paradise. Even the best security arrangements can fail due to a minor error if the personnel are not adequately trained and aware of it.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Healthcare Industry
Digital technology is essential for business operations at hospitals, acute care institutions, urgent care clinics, and physician offices. It is also necessary to ensure the smooth functioning of the hospital infrastructure, including HVAC, communications, and electrical systems.
Furthermore, a provider’s digital infrastructure is closely linked with various medical IoT devices. This extensive array of digital technology in healthcare includes multiple hardware, custom software development, and cloud services, making them all possible targets for hackers.
Cyber intrusions pose a serious risk to all aspects of care continuity, regardless of whether they are motivated by financial gain, a desire to impede the delivery of essential healthcare, or another goal. Therefore, cybersecurity in the healthcare industry is critical. To understand its importance, let’s look at the top components that healthcare cybersecurity must protect to prevent data breaches.
Key Systems and Data Healthcare Cybersecurity Experts Should Secure
Let’s examine some typical systems and devices that healthcare cybersecurity plans usually need to secure for a streamlined healthcare operation.
1. Email
Email inboxes contain information like patient data, even though you might not consider them a form of sensitive medical data. Hackers may use email as a means of attack to spread malware or carry out phishing campaigns. That is why email systems must be secured as part of cybersecurity for hospitals to prevent the theft of critical data.
2. Medical Devices
Hospitals and doctors’ offices use various medical equipment to provide care. Physicians may carry tablets to write prescriptions, while nurses use medical PC stations to monitor patient records. Malicious actors may obtain unauthorized access to the data on these devices if they aren’t properly secured or regularly updated. They might even install malware to launch remote attacks later. That’s why implementing robust healthcare cybersecurity solutions is essential to prevent unauthorized access and ensure all connected devices remain secure.
3. Connected IoT Devices
Healthcare businesses use a wide range of linked or smart devices in addition to standard IT equipment, such as elevator controllers and Internet-controlled HVAC sensors. These devices can be compromised if they are not adequately patched, protected, and monitored. You will need a strong healthcare data breach protection plan to avoid any contingencies.
4. Legacy Systems
Legacy systems refer to outdated software or technologies that no longer receive regular updates or security patches, leaving them highly vulnerable to cyberattacks. These systems often pose significant challenges, such as limited interoperability, security risks, and difficulty in maintenance.

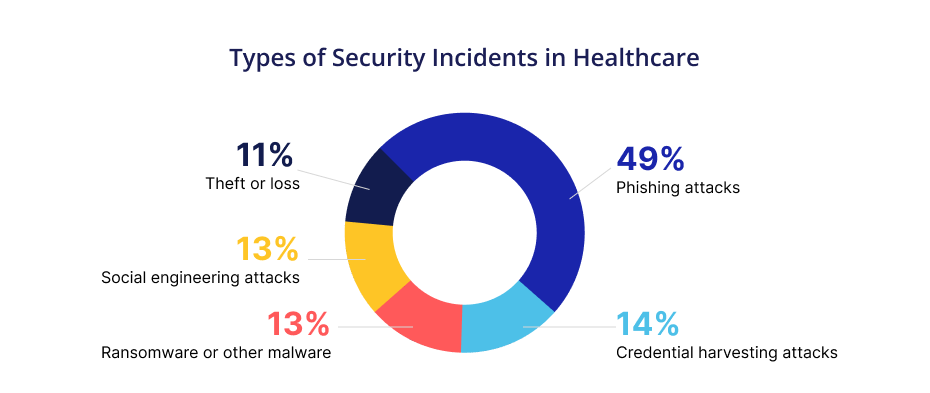
Common Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare
Healthcare businesses are experiencing an unprecedented number of breaches and attempted intrusions. This is mainly because hackers find healthcare data an alluring target. Attackers try to obtain valuable healthcare data using a range of methods. Some cybersecurity risks in healthcare include:
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a cyberattack where digital intruders deceive victims into divulging private information. To reveal usernames and passwords, they may send emails posing as IT personnel or include dangerous links. If the phishing attack in healthcare is successful, the hackers can use the private information to enter networks and steal information.
2. Malware Attacks
One of the most common cybersecurity threats in healthcare is malware attacks. It is malicious software designed to disrupt operations and allow hackers to access systems or data without authorization. Threat actors can use malware to gather information, take over computers, or disrupt services.
3. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks in healthcare happen when cybercriminals infect hospital or clinic systems with malicious software that locks or encrypts patient data. Attackers encrypt the victim’s files and then demand a ransom from the company to unlock them.
A hospital may suddenly lose access to critical systems like patient records, appointment schedules, or diagnostic tools. If the targeted organization lacks enough backups, it must pay the ransom. For example, in 2024, Change Healthcare faced a ransomware attack that affected more than 190 million people.
4. Insider Threats
Hospital employees and other staff members have authorized access to several systems. Employees put sensitive data at risk if they purposefully or unintentionally misuse those systems. Healthcare network security is impacted more if the systems are set up with extra permissions that provide internal users greater access than required.
5. System Vulnerabilities
System vulnerabilities may exist in recalled devices, out-of-date or unpatched software, and prohibited equipment. Public databases frequently publish information about vulnerabilities, manufacturers provide recall information, and agencies like the FDA give information on banned products. Hackers can quickly identify all this information to create cybersecurity issues in healthcare.
Best Practices to Strengthen Healthcare Network Security
All healthcare organizations should adhere to cybersecurity best practices to reduce the risk of breaches. Even if each company has different security requirements and hazards, they must follow the required guidelines. But how could they achieve that? Let’s check it below.
1. Ensure Asset and Data Visibility
If you can’t see it, you can’t protect it. That’s why the first step in healthcare IT security is knowing what’s in your system. To have comprehensive visibility, you must know every asset linked to your company’s network.
The data that devices gather, handle, or access, the healthcare services those assets offer, and the security measures that are (or are not) in place to protect the devices. Regular updates, data leakage monitoring, and tracking tools help spot hidden issues, old software, or weak points before they cause problems.
2. Implement Security Controls
Every healthcare business should ideally have basic and advanced cybersecurity measures. This ensures defense-in-depth, meaning another will take its place if one control fails. For instance, an anti-virus tool may prevent viruses from entering an organization’s firewall.
However, traditional tools alone may not be enough to tackle evolving cyber threats. Integrating AI development services can further strengthen cybersecurity by enabling intelligent threat detection and automated response systems. Healthcare cybersecurity requires a strong incident response plan to ensure that any security issues are either prevented or addressed quickly.
The following are the fundamental security measures:
- Antivirus software
- Data backup and restoration
- Data encryption (at rest and in transit)
- Firewall protection
- Incident response plan
- Rules and regulations
- Application security
- Vulnerability and patch management
The following are the advanced security measures:
- Multi-factor authentication
- Network segmentation
- Anti-theft devices
- Digital forensics
- Red teaming
- Segmentation of networks
- Sharing threat intelligence
3. Conduct Vulnerability Assessments & Penetration Testing (VAPT)
This is similar to hiring a professional hacker to access your system and find its vulnerabilities. VAPT services enable you to address issues before the attackers discover them. Frequent inspections maintain your healthcare information security.
4. Strengthen Endpoint & Network Security
You must secure each computer, tablet, or other device that connects to your network. A single loophole allows hackers to enter covertly. Therefore, it’s critical to consult healthcare cybersecurity services to close all gaps so hackers don’t create havoc.
5. Secure IoT & Medical Devices
Although smart medical devices like infusion pumps and heart monitors are helpful, hackers may target them by taking advantage of weak security measures or outdated firmware. Ensuring healthcare IoT security prevents them from being used to steal confidential information or harm patients, keeping both individuals and information safe.
6. Train Healthcare Staff on Cyber Hygiene
Even the most incredible technology cannot prevent a careless click. Data protection greatly benefits from training administrators, nurses, and physicians to recognize fraud, create secure passwords, and employ safe internet practices.
7. Implement an Incident Response Plan
What if the security issues still persist? Well, in that case, a systematic incident response plan can help. Think of it as a fire drill for cyberattacks. Everyone is aware of what to do, who to contact, and how to swiftly control the issue to reduce downtime and damage.
Crucial Compliance Standards for Cybersecurity in Healthcare
Safeguarding patient data is as vital as administering care in the medical field. Laws, regulations, and certifications have been established to enhance cybersecurity for healthcare. Below are the key laws and frameworks healthcare organizations must comply with to ensure robust data protection.
1. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a United States statute that safeguards patient health information. It ensures the confidentiality and security of medical records at clinics, hospitals, and insurance providers. The main goal is to ensure your data doesn’t get misused. HIPAA cybersecurity compliance offers specific guidelines and policies to safeguard patient information.
(a) HIPAA Privacy Rule
It includes all the covered entities (healthcare clearinghouses, health plans, and healthcare providers) to ensure they securely handle, store, and transmit protected health information (PHI) and comply with HIPAA regulations.
Key Provisions:
- Patients can view their health records, ask for changes, and decide who can see their information.
- Healthcare providers must provide a Notice of Privacy Practices (NPP) that explains how they use and protect your health information.
- Requires a Notice of Privacy Practices (NPP) to be shared with patients.
(b) HIPAA Security Rule
The HIPAA Security Rule establishes guidelines for protecting electronic PHI (ePHI) and applies to covered entities and business associates.
Key Safeguards:
- Administrative (e.g., workforce training, risk analysis)
- Physical (such as workstation security and facility access controls)
- Technical (such as audit controls, access control, and encryption)
(c) HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
The goal of the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule is to mandate that covered organizations notify the Secretary of HHS (if a breach involves 500 or more individuals), impacted parties, and the media of a breach involving unsecured PHI.
Key Points:
- If someone breaches your health data, the provider must tell you within 60 days.
- Business associates must inform covered entities of a data breach.
2. HITRUST CSF (Common Security Framework)
The Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST) is a non-profit group that helps companies protect data, follow rules, and reduce security risks. HITRUST’s CSF includes internationally accepted security frameworks such as ISO27001 and NIST 800-53. It works with experts to spot and handle new threats.
3. Protected Health Information (PHI)
Protected health information (PHI), as defined by HIPAA and its Privacy Rule, is any data that must be secured and protected to preserve a patient’s privacy about their medical treatment. Healthcare providers must protect your health information, whether it’s from the past, present, or future.
4. General Data Protection Regulation
The GDPR is primarily a European regulation. Thanks to it, people have control over how their personal data is used. In the context of healthcare, this implies that physicians and hospitals must obtain consent before collecting any data and provide a clear explanation of what they are collecting and why.
5. ISO 27001 for Healthcare Security
ISO 27001 sets global rules that help healthcare providers keep patient information safe and secure. It is a set of best practices for protecting patient records, so nothing is left to chance when it comes to privacy and data security.
Adhering to HIPAA compliance and cybersecurity standards can help healthcare firms prevent expensive data breaches and protect information. These regulations are necessary to create safer, more intelligent, and more reliable cybersecurity for hospitals and healthcare facilities.
Major Cybersecurity Challenges in Healthcare
There are several problems and obstacles in healthcare cybersecurity, some of which are specific to the sector. These consist of:
1. Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare institutions must comply with numerous privacy and security laws, including HIPAA, HITRUST, and more. Non-compliance can result in harsh penalties. Many healthcare institutions fail to ensure compliance due to a lack of cybersecurity consulting, limited staff training, and inadequate regulatory understanding.
Healthcare providers must seek the right expertise and support to bridge these critical gaps. They can work with an HIPAA compliant app development company with expertise in building compliance-driven healthcare apps. They’ll help you stay updated, avoid mistakes, and keep your healthcare data safe and compliant at all times.
2. Budget Constraints
One of the biggest cybersecurity challenges in healthcare is the high cost of implementation. Smaller healthcare providers often don’t have big budgets for cybersecurity, which can make it harder for them to stay fully protected. Because of this, investing in the infrastructure monitoring, technology, and qualified staff required to maintain strong security may be challenging.
You can start small with scalable cybersecurity solutions that fit your budget. Use cost-effective cloud security services and open-source platforms. Start by securing the most at-risk parts of your system, then keep improving your protection over time.
3. Lack of Self-Awareness
Insufficient cybersecurity knowledge and training among healthcare personnel may result in human error-driven vulnerabilities, such as falling for phishing scams or improperly handling private information.
Healthcare companies can teach their staff the basics of staying safe online, such as spotting fake emails, using strong passwords, and handling patient info carefully. Short, simple training sessions can really help everyone stay alert and avoid costly mistakes.
4. Medical Device Vulnerabilities
Many medical devices connect to the internet but don’t always come with built-in security, which can leave them open to cyber threats. Cybercriminals may target these healthcare IoT vulnerabilities to obtain private information or interfere with medical care.
Regularly update the security on medical IoT devices and always use strong, hard-to-guess passwords. Keep them on a separate network so hackers can’t access everything. Also, choose devices from companies that care about security.
5. Third-Party Risks
Healthcare providers work with several third-party vendors, like device makers and billing services. If those companies don’t secure their systems, they can pose cybersecurity risks in the healthcare sector.
Only work with trusted partners who keep their systems secure. Before sharing any patient data, make sure they follow safety rules. Keep checking on them to be sure your data stays protected.
6. Retention of Cybersecurity Talent
Given the tremendous demand for qualified cybersecurity experts across all industries, it can be difficult for healthcare firms to recruit and retain these people.
Focus on what matters. You can offer a friendly work environment, fair pay, and chances to learn and grow. You can always team up with cybersecurity services that protect your healthcare organization’s data.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Healthcare and Emerging Trends
Till now, you must have understood everything from threats to compliance to best practices in healthcare. In this section, we will see the cybersecurity trends in healthcare that are driving the industry. So, let’s move ahead.
1. Increased Adoption of AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning in healthcare are being widely used in strategies and tactics to eliminate cyber threats in real time. Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity can recognize the indications of a security breach and notify the concerned authorities.
For example, machine learning development for healthcare can easily recognize suspicious trends, like logging in from a restricted IP address or at strange hours, as danger. Apart from that, AI in healthcare can spot unusual activity like someone accessing too much data too quickly and raise an alert right away.
2. Blockchain Technology for Data Security
Blockchain for healthcare encrypts patient records using a distributed ledger that is impossible to change. It makes it easier for healthcare businesses to manage data in the way that they need to. Since anybody with a network connection can observe any changes in the data, it may lessen the possibility of unwanted access to patient records and ensure their integrity.
3. Focus on Zero Trust Architecture
A security concept known as “Zero Trust” is based on the idea that no network, person, or system should be regarded as reliable simply because it is part of the internal network.
According to Zero Trust, all recognized users of a company’s network or data must pass an authentication process and be given access to only the information required to perform their jobs.
Therefore, healthcare institutions have started incorporating zero-trust models and data security services to reduce the opportunities provided for unauthorized individuals.
4. Quantum Cryptography Encryption
A relatively recent development in cryptography, quantum cryptography, creates unbreakable security keys by utilizing quantum mechanics. As hackers develop more effective ways to break the standard encryption technique, quantum cryptography might be a powerful way to prevent future cyber threats in healthcare.
5. Biometric Authentication for Enhanced Security
Biometric authentication is more difficult to hack than password control systems, and fingerprint, facial recognition, or even iris scans are more trustworthy than passwords. In the context of healthcare institutions, biometric authentication can help safeguard access to critical data and restrict access to individuals’ personal information to authorized staff members.
Get End-to-End Cybersecurity for Healthcare with SparxIT
At SparxIT, we understand how important it is to keep patient data safe, especially in healthcare, where even the slightest mistake can have big consequences. That’s why we offer innovative and reliable cybersecurity solutions made just for hospitals, clinics, and healthcare platforms.
As a leading healthcare app development company, we protect your medical devices to secure digital patient records. But we don’t stop there. We know that people are just as important as technology. So, we also help train your staff to spot risks and respond quickly to anything suspicious.
And if something does go wrong? We’re ready. Our quick-response plans help you act fast and stay in control. At SparxIT, we’re here to keep your systems safe, your team prepared, and your patients’ trust protected every step of the way.

Partner with Experts
Frequently Asked Questions
How does AI help in improving cybersecurity in the healthcare industry?





AI helps improve cybersecurity by quickly identifying threats and noticing any unusual activity as it happens. Moreover, it automates responses to reduce human error. It strengthens system defenses by continuously learning from new attack methods, helping healthcare organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
What are the most common cyber threats in healthcare industry?








The most common threats include phishing attacks, ransomware, insider threats, data breaches, and attacks on outdated legacy systems. These threats often aim to steal or encrypt patient data, disrupt operations, or demand ransom from healthcare providers.
What are the benefits of using AI in healthcare cybersecurity?








Artificial intelligence and cybersecurity combined offer faster threat detection, real-time monitoring, automated incident response, and predictive analytics. This helps secure connected devices, reduce false alarms, and optimize resources, making cybersecurity in healthcare resilient.



