Data integrity, the completeness and accuracy of sensitive user data, is a concern across industries with cyberattacks becoming sophisticated. Weak points and vulnerabilities within the system often result in tampering and data breaches. Since these result in immense data loss, brand reputation damage, and hefty penalties, industries are taking strict measures to defend themselves.
The case is similar to the healthcare industry, with HIPAA and GDPR compliance guarding patient data. Many healthcare practitioners are abandoning on-premise models and going for cloud security in healthcare. This way, ensuring data security and complying with regulatory adherence becomes straightforward for them. In doing so, they also eliminate on-premise risks, prevent data breaches, and upscale their healthcare model.
As modernization is taking place, it becomes imperative for healthcare organizations to rely on experts during the shift while maintaining data integrity. In that case, these practitioners are outsourcing cloud computing security services and bolstering their existing cloud infrastructure or migrating to one with valuable healthcare-focused insights.
Considering that you are among the healthcare decision-makers comprehending the necessity of cloud security for healthcare, this bifurcation can assist you. With the benefits, common threats, probable best practices, and systematic approach for data protection, this cloud security guide assists in making better healthcare-focused decisions.
What is Cloud Security in Healthcare Sector?
When we talk about cloud security in healthcare, it sheds light on the set of compliance policies, cognitive technologies, and data protection practices designed to protect the healthcare industry. Given the sensitive nature of healthcare data, such as patient records and medical histories, cloud security ensures that this data is kept secure, compliant with regulations, and available when needed.
That can be done with real-time monitoring, vulnerability identification, end-to-end encryption and access control, and regular assessment of third-party cloud systems. While being generic, these apply to the healthcare industry with confidentiality, addressing the data integrity issue.
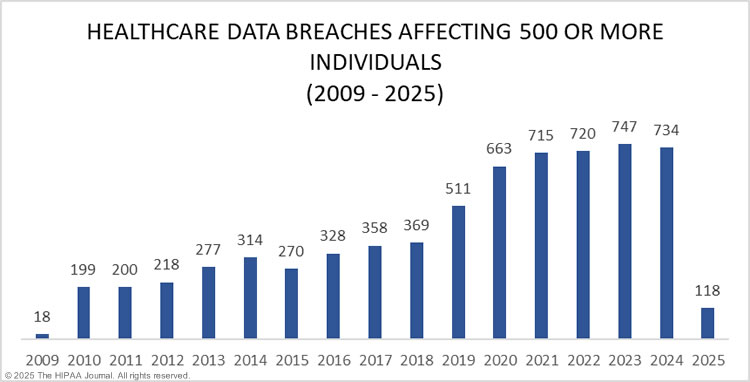
Since 2009, the industry has witnessed 6,759 data breaches, affecting approximately 846,962,011 individuals. This figure brings the adversity of users and at stake information, ultimately navigating the healthcare industry to shift to cloud computing for safety and tamper-proof protection.
Types of Cloud Security in Healthcare Industry
Now that the premise is set about the reasoning towards this protection-focused shift, it becomes a necessity to apprehend types of healthcare cloud security. Since these can be diversified based on the data, individual healthcare practitioners choose cloud transformation services to focus on the benefits that they pose.
| Cloud Security Type | Key Features | Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare | Unique Advantage |
| Public Cloud Security Services | Shared cloud resources, managed security by provider | Cost-effective, scalable, and compliance-ready | Access to advanced security tools |
| Private Cloud Security Services | Dedicated infrastructure, customized security | Higher security, full compliance control | Enhanced data privacy & customization |
| Hybrid Cloud Security Services | Mix of public & private cloud, flexible security | Balance of security & scalability, disaster recovery | Optimal resource utilization |
| Multi-Cloud Security Services | Multiple cloud service providers for healthcare, distributed security | Reduces provider dependency, improves availability | Improved redundancy & performance |
Based on this table, healthcare practitioners can categorize themselves and find out which types fit their needs. No two businesses can have absolutely the same requirements. This brings them to this table to align the requirements and choose the types that fit them best.
Common Healthcare Data Security Threats
As the cyberattacks are becoming sophisticated based on the inclination towards intelligent technologies, it is becoming more unyielding to defend against them. Along with that, system vulnerabilities are contributing factors to the risked safety.
However, another reason can be that healthcare practitioners are not aware of the healthcare IT security threats. That being said, the mandatory need to understand against what threats to defend can assist in making better security-focused decisions. These below-mentioned attacks are among the many that are causing organizations to become prone to data breaches.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks, as they sound, are exactly about asking for ransom for a decryption system. To bring a clear understanding, resulting from unauthorized data access, hackers encrypt healthcare data with malicious software. To decrypt it, they ask for ransom in terms of money or different data.
Phishing & Social Engineering
Among the many cloud security risks in healthcare industry, phishing is a workforce-focused cyberattack. In this, the cyber attackers send deceptive emails or messages on social media that lead the workforce to click it. Just one click leads to either installing malware in the system or making a vulnerability breakpoint for them to access the system logins.
Insider Threat
Healthcare organizations sometimes come across insider threats, an employee or contractor misusing the patient data, that can cause them brand reputation damage. To be precise, an insider with data access to confidential information can leak it or manipulate it to benefit them.
Unauthorized Access
As the insider access roots from unauthorized access, many other complications and vulnerabilities leading to data breach arise from this. To say that NDA signed information or sensitive patient data can be misused, the healthcare cyberattackers retrieve it from healthcare solutions with negligible data access security.
Misconfigured Cloud Storage
Among the many cloud security risks in healthcare industry, this arises from the third-party vendor’s cloud-based medical record storage or the organization’s private system. Errors, glitches, or gaps in the cloud-based environment lead to cyberattack exposure and, furthermore, lead towards breaches.
How to Ensure Cloud Security in Healthcare?
Having understood all threats, the fundamental concern becomes how to secure the cloud systems. For that, apprehending cloud security best practices for healthcare becomes imperative. These are the building blocks of how to leave no space for vulnerabilities and deter any possible cyber threat.
1. End-to-End Data Encryption in Healthcare Cloud
Data encryption ensures that data remains unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have authorization. Whether stored in the cloud (at rest) or transferred between systems (in transit), encryption protects sensitive information from cyber threats. Strong encryption protocols like AES-256 and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are commonly used in healthcare.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication in Healthcare Cloud
A password alone isn’t enough when it comes to data security. To safeguard the cloud system and patient data, MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using an additional method, like an OTP (one-time password), fingerprint, or facial recognition. This prevents unauthorized access even if login credentials are compromised due to phishing.
3. Automatic Abnormal Detection
Cybersecurity threats don’t always come with warning signs. Since the technology has reached a new spectrum, AI-powered security tools can analyze system behavior and detect unusual activities, such as unexpected login attempts or large data transfers, before they become security incidents. This early threat detection assists in preventing breaches in real time and defends healthcare organizations.
4. Access Control & Role-Based Permissions
Not everyone in a healthcare organization needs access to all data. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel, such as doctors, nurses, or administrators, can access the specific patient information they need based on the subsequent treatment. This reduces the risk of internal data leaks and unauthorized exposure and ensures patient data protection in the cloud.
5. Regular Security Audits & Compliance Checks
Security is not a one-time setup but a vigilant process that requires monitoring, assessment, and remediation. Continuous audits help pinpoint vulnerabilities and ensure that cloud infrastructure meets regulations with HIPAA compliance consulting. Routine compliance checks also keep organizations up to date with the latest security standards.
6. Cloud Monitoring & Threat Detection
Real-time monitoring and threat detection are required to track and analyze security events across cloud systems. Security teams utilize automated tools to detect anomalies, flag suspicious activity, and enhance the response to an incident before an attack escalates. With continuous monitoring strengthening the overall security posture, you can deter penalty-prone cyberattacks.
7. Zero Trust Security in Healthcare Cloud
Instilling the verification-and-approve-focused ideology pays in the long term. That comes with the Zero Trust security that follows the principle of “Never Trust, Always Verify.” Every access request, whether from inside or outside the organization, is continuously verified, reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized data exposure.
8. Biometric Authentication
Biometric security, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, presents healthcare organizations with an extra layer of identity verification. Unlike passwords, incorporating biometric data into cloud security solutions for protecting patient data is unique to each individual and cannot be easily replicated, making it an effective safeguard for healthcare systems.
Challenges of Data Security and Cloud Computing in Healthcare
After providing you with the threats and how to safeguard against them, we have reached the healthcare data security challenges that are to be comprehended well. Before implementing strategies or making cloud environment shifts, the healthcare industry must get familiarized with these and find the apt way to overcome them.
Data Privacy Concerns
It is a known fact that healthcare data is highly sensitive, containing patient records, medical histories, and financial details. Unauthorized access, data leaks, or improper handling can put patient privacy at risk along with the healthcare organizations’ reputation. It is mandatory to ensure that data is only accessible to authorized personnel through encryption, access controls, and compliance policies, which is essential to maintaining trust and confidentiality.
Cybersecurity Threats
With cyberattacks on the rise, healthcare organizations face threats like ransomware, phishing, and data breaches. Attackers often target hospitals and clinics because their data is valuable and critical for patient care. Implementing multi-layered healthcare data security in cloud, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and real-time monitoring, helps mitigate these risks.
Regulatory & Compliance Issues
Healthcare organizations and practitioners must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA (USA), GDPR (Europe), and HITECH to protect patient data. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, brand reputation damage, patient data loss, and legal consequences. However, navigating these regulations can be complex, especially when working with third-party cloud providers. Organizations must ensure that their cloud security policies always align with compliance requirements.
Cloud Downtime & Reliability Issues
Managed cloud services for healthcare provide scalability and accessibility, but downtime and service disruptions can impact healthcare operations. A system failure or an outage can delay access to critical patient records, affecting treatment decisions. Disaster recovery plans, backup systems, and choosing reliable cloud providers help reduce the risks associated with downtime.
Data Migration Risks
Moving healthcare data from on-premises systems to the cloud or switching between cloud providers can be challenging and risky. Data loss, corruption, or misconfiguration is always possible during healthcare cloud migration security. Proper data validation, encryption during transfer, and phased migration strategies help ensure a smooth and secure transition.
Emerging Trends for Cloud Computing in Healthcare for 2025
In cloud computing in healthcare, addressing security, compliance, and reliability concerns needs to be prioritized. The intelligent advancements in technology, like ML, IoT, VR, edge computing, and AI in healthcare, are assisting in overcoming these cloud security-focused challenges while ensuring efficiency enhancement and security of healthcare systems. Here’s a look at the key trends shaping cloud computing in healthcare for 2025.
1. AI & Machine Learning in Cloud Security
The emphasis on the sophistication of Cybersecurity threats is imperative as it leads to inefficient manual security monitoring. AI and machine learning assist by recognizing patterns, detecting anomalies, and predicting potential breaches before they locate a vulnerable endpoint. These intelligent technologies allow cloud systems to pinpoint and respond to threats in real time, strengthening overall security.
2. Blockchain Technology
Ensuring data privacy and security in cloud-based healthcare are among the immense challenges in cloud computing. Blockchain technology creates tamper-proof digital records, ensuring that patient data remains unaltered and traceable, building a secure layer. By decentralizing healthcare data, blockchain reduces the risks of unauthorized access, fraud, and data manipulation.
3. Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Strategies
Relying on a single cloud provider can lead to downtime risks, vendor lock-in, and compliance challenges. Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies allow organizations to distribute workloads across multiple cloud environments, ensuring greater reliability, flexibility, and better control over cloud security in healthcare sector.
4. Edge Computing in Healthcare
Cloud downtime can disrupt patient care, especially in remote areas. Edge computing processes data closer to where it is generated, whether in hospitals, wearable devices, or IoT-enabled medical equipment. This reduces latency, improves data and cloud security in the healthcare industry, and ensures real-time access to critical healthcare data even in case of network failures.
5. Healthcare Cybersecurity
With cyber threats increasing, healthcare organizations are integrating advanced security solutions like biometric authentication, AI-driven threat detection, and automated security audits. These innovations help bolster cloud defenses, prevent breaches, and ensure compliance with identifying shortcomings and remediating them.
6. AR/VR in Healthcare
AR/ VR in healthcare are no longer just futuristic concepts. They are transforming medical training, remote surgeries, and patient rehabilitation. Cloud computing enables AR/VR applications to process and store large datasets efficiently, making advanced healthcare solutions more accessible.
Popular Tools for Cloud Data Security in Healthcare
Healthcare and cloud computing go hand in hand considering the HIPAA compliance in place. This results in the need for robust security measures, and it has never been greater. With data privacy concerns, cybersecurity threats, compliance complexities, and cloud downtime risks, securing patient information remains a top priority.
Fortunately, emerging technologies such as AI-driven security, blockchain for data integrity, zero-trust architecture, and edge computing are reshaping cloud security strategies. By integrating advanced cloud-based healthcare solutions, practitioners can overcome these challenges, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected while maintaining reliability, compliance, and efficiency in cloud environments. Let’s explore some of the key software solutions and tools that are transforming cloud data security in healthcare.
| Category | Top Cloud Security Tools for Healthcare | Function |
| Cloud Security & Compliance | AWS Shield, Azure Security Center, Google Cloud Security | Protects against threats and ensures compliance. |
| Data Encryption & Privacy | VeraCrypt, BitLocker, Kaspersky Security Cloud | Encrypts sensitive healthcare data. |
| Identity & Access Management (IAM) | Okta, Auth0, Microsoft Active Directory | Manages secure user access and authentication. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Symantec DLP, McAfee DLP, Forcepoint DLP | Prevents unauthorized data access and leaks. |
| Threat Detection & Monitoring | Splunk, Prisma Cloud, Trend Micro | AI-powered real-time threat detection. |
| Blockchain for Security & Integrity | Hyperledger, Ethereum, IBM Blockchain | Ensures secure, tamper-proof patient records. |
| Secure API Management | Apigee, AWS API Gateway, Postman | Protects and manages healthcare API interactions. |
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Integrating cloud computing in healthcare has catalyzed a paradigm shift in how medical data is managed, shared, and secured. With an ever-expanding digital footprint, healthcare organizations must navigate stringent security requirements, compliance mandates, and data integrity concerns.
Cloud technology, when fortified with advanced security frameworks, presents a robust infrastructure that not only safeguards patient data but also augments operational efficiency, ensures regulatory adherence, and mitigates cybersecurity risks. Below are the key benefits of cloud security for healthcare organizations, each playing a crucial role in fortifying the industry’s digital ecosystem.
1. Enhanced Patient Data Protection in the Cloud
With an exponential upsurge in patient data being stored and processed, cloud computing presents an advanced security framework to shield sensitive health records from unauthorized access. A cloud computing company hired by a healthcare practitioner implements multi-layered encryption, role-based access control (RBAC), and end-to-end data protection measures to ensure that medical records remain invulnerable to breaches.
2. Healthcare Data Breach Prevention
Healthcare remains a prime target for cybercriminals due to the value of patient data on the black market. Cloud computing leverages next-generation cybersecurity solutions such as Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and AI-powered threat intelligence to preemptively identify and neutralize threats before they escalate. Additionally, disaster recovery protocols and immutable healthcare cloud backup solutions ensure that even in the event of a security incident, data remains retrievable without compromise, minimizing operational disruptions.
3. HIPAA Compliance in Cloud Security
Regulatory compliance is a mandatory element of healthcare cloud security, with compliances such as HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH governing how patient data must be handled.
Cloud providers offer pre-configured compliance frameworks to healthcare organizations, ensuring they adhere to strict security standards. Features such as audit logging, automated compliance reporting, and encrypted data storage facilitate seamless regulatory adherence while reducing administrative overhead.
4. Scalable Healthcare Cloud Infrastructure Security
Unlike static on-premise systems, cloud services for healthcare upscales based on an organization’s evolving needs. This scalability extends beyond storage and processing power and bolsters security, eventually benefiting telemedicine, AI-powered diagnostics, and real-time patient monitoring, where data transmission volumes vary significantly.
5. Reduced On-Premise Security Risks
Cloud solutions for healthcare facilitate secure cross-institutional data sharing through encrypted APIs, federated access controls, and blockchain-focused verification protocols. This ensures that authorized professionals can securely access electronic health records (EHRs), diagnostic imaging, and real-time patient vitals without compromising confidentiality.
Regulatory Compliance Cloud Security Standards for Healthcare
Compliance is essential in healthcare cloud security, ensuring patient data privacy, secure storage, and ethical handling. Regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH set strict standards for data encryption, access control, and breach prevention. These frameworks help healthcare organizations align with legal mandates while safeguarding sensitive information.
The table below outlines key cloud security standards for healthcare, their purpose, and how they enforce security policies.
| Healthcare Cloud Compliance | Purpose | Key Focus Areas |
| HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) | Protects Electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) | Encryption, access control, audit logs |
| HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act) | Strengthens HIPAA enforcement | Breach notifications, stricter penalties |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Provides risk-based security guidelines | Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover |
| SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) | Assesses cloud security controls for service providers | Confidentiality, integrity, availability |
| FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program) | Ensures cloud security compliance for federal agencies | Cloud vendor assessment, risk management |
| PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) | Secures healthcare-related online payments | Cardholder data protection, fraud prevention |
Why Choose SparxIT Among the Trusted Cloud Service Providers for Healthcare?
Securing patient data while ensuring regulatory compliance, scalability, and seamless interoperability is a significant challenge for healthcare organizations. To overcome them, SparxIT, a trusted pioneer among the cloud service providers for healthcare, addresses these concerns with end-to-end cloud security solutions built on HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH-compliant frameworks.
With intelligent technologies like AI, blockchain, and edge computing, SparxIT enhances interoperability, secure data sharing, and fraud prevention. By choosing us, healthcare providers gain a future-ready cloud partner dedicated to security, compliance, and innovation, ensuring a digitally transformed and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem.

Partner with Experts
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of HIPAA compliance in cloud security?







HIPAA ensures secure storage, processing, and transmission of patient data. At SparxIT, we implement HIPAA-compliant encryption, access controls, and audit mechanisms to protect sensitive medical information while maintaining regulatory compliance.
What are the healthcare data security challenges?












Challenges include cyber threats, data breaches, and compliance risks. SparxIT mitigates these with multi-layered encryption, AI-powered threat detection, and automated compliance audits, ensuring a secure and resilient cloud environment.
What are the latest trends in healthcare cloud compliance for security?












Trends include Zero Trust architecture, blockchain for data integrity, hybrid-cloud strategies, and 5G-enabled security. SparxIT integrates these innovations to enhance compliance, secure data sharing, and real-time threat monitoring.
How does cloud data security in healthcare differ from other industries?












Healthcare handles highly sensitive patient data under strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. SparxIT ensures Zero Trust security, AI-driven threat detection, and secure interoperability, making healthcare cloud security more complex yet highly secure.
How do AI and machine learning impact cloud security in healthcare industry?












AI enhances predictive threat analysis, anomaly detection, and compliance automation. SparxIT leverages AI-driven cybersecurity to prevent breaches, detect threats in real time, and optimize cloud security.


